Home
Technical Design Document Template
A structured Technical Design Document template to guide the design, implementation, and testing of new software features or systems, fostering collaboration and ensuring project success.
Get things done with NotePlan
Categories
What is Technical Design Document?
A Technical Design Document (TDD) is a detailed blueprint that outlines the technical specifications and implementation plan for new software features, systems, or entire applications. It serves as a central reference point for developers, designers, testers, and stakeholders, ensuring everyone shares a common understanding of the project's technical goals and how they will be achieved.
The TDD typically includes sections on the project's purpose, objectives, architecture diagrams, detailed design of components, implementation steps, testing strategies, and revision history. By addressing potential challenges early in the design phase and providing a structured plan for development, the TDD helps mitigate risks, streamline collaboration, and ensure the successful delivery of a high-quality software product.
When should you create Technical Design Document?
Technical Design Documents (TDDs) are typically created in the early stages of a software development project, after the initial requirements gathering and analysis phase. This is when you have a clear understanding of the problem you're trying to solve and the high-level goals of the project. Creating the TDD at this point helps to:
- Solidify the Solution: The process of writing a TDD forces you to think through the technical details of the solution, ensuring that it is feasible and meets the project requirements.
- Align the Team: The TDD serves as a shared reference point for the development team, ensuring that everyone is on the same page regarding the technical direction of the project.
- Mitigate Risks: By identifying potential problems early on, the TDD helps to mitigate risks and prevent costly rework later in the development process.
- Estimate Effort and Timeline: The TDD provides a basis for estimating the effort and timeline required to implement the solution.
Here are some specific scenarios where creating a TDD is particularly beneficial:
- Complex Projects: If the project is complex or involves multiple teams, a TDD is essential for coordinating efforts and ensuring that all components work together seamlessly.
- New Technologies: If the project involves using new or unfamiliar technologies, a TDD can help to clarify the technical approach and identify potential challenges.
- High-Risk Projects: If the project has a high risk of failure, a TDD can help to identify and mitigate potential problems early on.
- Projects with External Stakeholders: If the project involves external stakeholders, a TDD can help to communicate the technical approach and get buy-in from all parties.
In general, it's a good practice to create a TDD for any project that is expected to take more than a few days to complete. Even for smaller projects, a TDD can be a valuable tool for clarifying the technical approach and ensuring that the project stays on track.
What are the benefits of Technical Design Document?
Technical Design Documents (TDDs) are invaluable assets in software development, bringing a host of benefits to teams, projects, and stakeholders. They foster a shared understanding of the project's technical vision, leading to smoother collaboration and informed decision-making. By identifying potential issues early on, TDDs enable proactive risk mitigation and reduce the need for costly rework later in development. They also facilitate accurate estimations of effort, timeline, and resources, ensuring projects stay on track. Additionally, TDDs promote transparency by providing stakeholders with clear insights into the technical aspects, fostering trust and enabling early feedback. Some of the benefits include:
- Shared understanding and improved communication among team members.
- Proactive identification and mitigation of technical risks.
- Informed decision-making based on a solid technical foundation.
- Reduced rework and improved development efficiency.
- Accurate estimations of effort, timeline, and resources.
- Enhanced product quality through thorough testing strategies.
- Clear documentation for future reference and maintenance.
- Increased transparency and trust with stakeholders.
- Facilitated early feedback for timely adjustments.
- Measurable progress tracking for effective project management.
About this template
Introduction
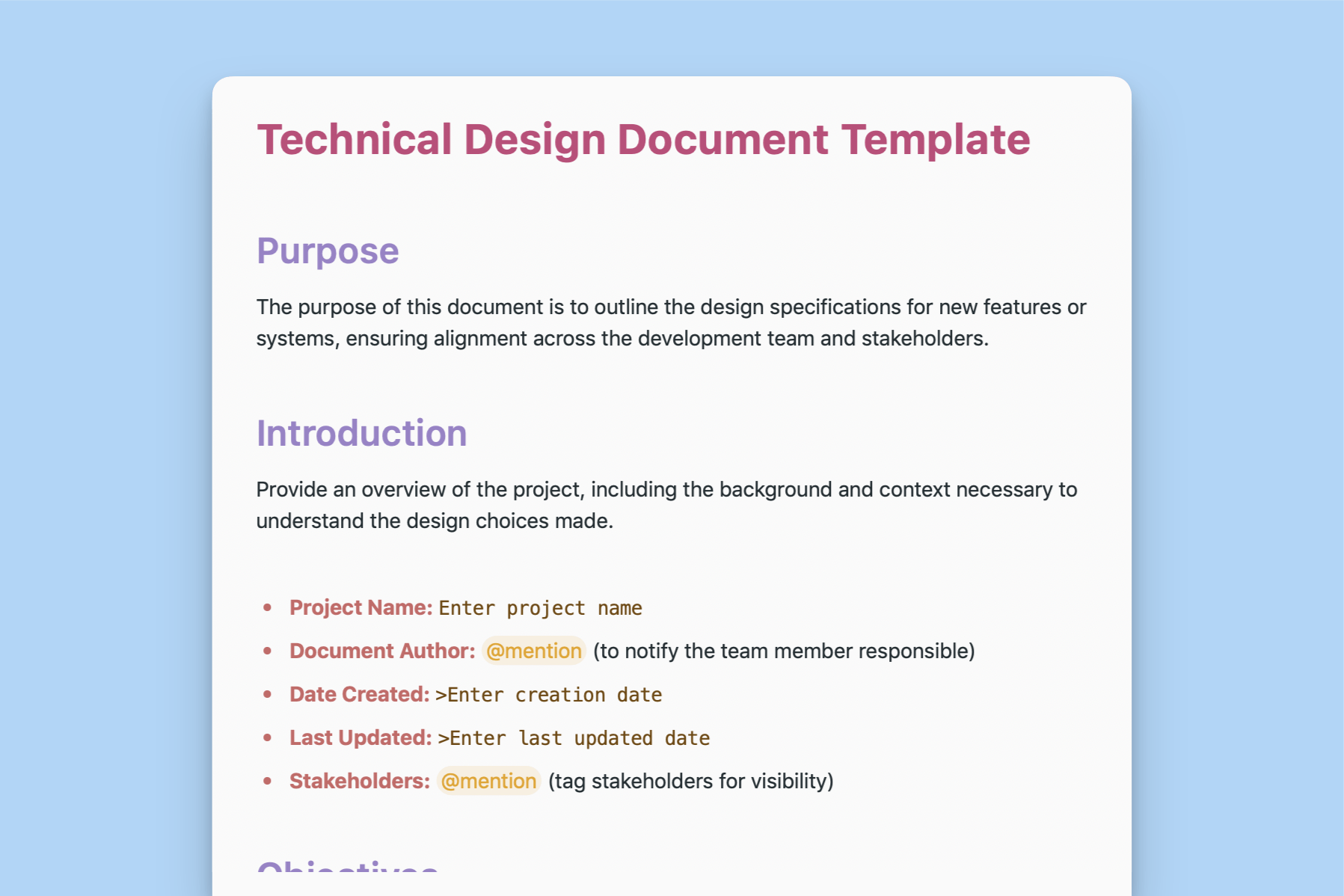
The Introduction section provides a succinct overview of the project, setting the stage for the detailed information that follows. It includes essential background information and context to help readers understand the rationale behind the design decisions. This section also includes specific metadata about the project, such as:
- Project Name: Clearly state the name of the project to avoid any confusion.
- Document Author: The person responsible for the document, identified using @mention for easy reference and notification.
- Date Created: The initial creation date of the document.
- Last Updated: The most recent date when the document was updated.
- Stakeholders: List of key stakeholders, tagged with @mention to ensure visibility and engagement.
Objectives
The Objectives section lists the primary goals and objectives the design aims to achieve. This part ensures that everyone understands the core purpose and priorities of the project. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Examples of objectives include:
- Objective 1: Describe the primary goal, such as improving system performance or adding a new feature.
- Objective 2: Outline secondary goals, such as enhancing user experience or ensuring scalability.
Architecture Diagrams
In the Architecture Diagrams section, visual representations of the system's high-level architecture are provided. These diagrams help in understanding how different components interact and how the system is structured. Links to these diagrams should be included for easy access and reference. Key diagrams include:
- System Overview Diagram: A high-level diagram showing the overall structure and major components of the system.
- Component Interaction: Diagrams illustrating how different components of the system interact with each other.
Design Details
The Design Details section delves into the specific design specifications of the system or feature. This section is divided into sub-sections for different components to ensure clarity and organization. Each component should be described in terms of:
- Description: A brief overview of the component.
- Responsibilities: Detailed explanation of what the component is responsible for.
- Dependencies: Any other components, systems, or libraries that this component depends on.
Implementation Plan
The Implementation Plan outlines the steps required to implement the design. This section helps in tracking progress and ensuring that the implementation follows a structured approach. Each step should be clearly described to provide a roadmap for developers. For example:
- Step 1: Description of the first implementation step, such as setting up the development environment.
- Step 2: Description of subsequent steps, detailing the progression of the implementation process.
- Step 3: Continue listing all necessary steps until the implementation is complete.
Testing Strategies
The Testing Strategies section describes how the design will be validated to ensure it meets the specified requirements. Different types of testing should be covered, including:
- Unit Testing: Plans for testing individual components in isolation, along with the tools to be used.
- Integration Testing: Strategies for testing how components work together as a system.
- Performance Testing: Specifications for performance benchmarks and the methods to test them.
Revision History
The Revision History section keeps track of all changes made to the document. This helps in maintaining a clear record of the document's evolution and ensures transparency. Each entry should include:
- Date: When the change was made.
- Version: The version number of the document after the change.
- Author: The person who made the change, identified using @mention.
- Description: Brief description of what was changed.
Comments and Discussions
The Comments and Discussions section facilitates ongoing dialogue and feedback regarding the document. Using @mentions and tasks, team members can request feedback, discuss integration points, and address potential issues. This section ensures continuous collaboration and improvement of the document.
- Feedback Request: @mention to request input from a specific team member.
- Discussion: Points for discussion, including potential issues and integration concerns.
Pro Tips:
- Regularly Update: The TDD is a living document. Update it as decisions are made and designs evolve to maintain accuracy.
- Tailor to Your Needs: Adapt this template to suit the specific requirements of your project. Add or remove sections as needed.
- Collaborate: Encourage active participation from all team members. Use the commenting features to gather feedback and ensure alignment.
- Review Thoroughly: Conduct formal reviews of the TDD before moving to implementation to catch potential flaws and inconsistencies.
By following this comprehensive TDD template, you can significantly increase the chances of delivering a successful software project that meets or exceeds expectations.